Table of Contents
-
Definition and Overview of Hyperthyroidism
-
Understanding the Thyroid Gland
-
What Causes of Hyperthyroidism
-
Signs and Symptoms
-
Diagnosis and Evaluation of hyperthyroidism
-
Treatment Options
-
Conclusion
Introduction
In this blog post we will discuss hyperthyroidism, what cause it, signs of it, and how to treat it. I know the read hyperthyroidism is a word that sounds complicated, but it will be broken down to make it super easy to understand.
Have you not been feeling yourself lately? Have you been feeling extremely tired, feeling hot all the time, trouble sleeping or having shaky hands or trembling? There could be many reasons why you are having these symptoms, but you might want to consider that you may be suffering with hyperthyroidism.
 What Is Hyperthyroidism?
What Is Hyperthyroidism?
Hyperthyroidism is defined as the elevated thyroid hormones levels which is called an overactive thyroid. Your body has this tiny organ called the thyroid gland. Think of it as a car accelerator which controls how fast or slow things happen in the body and it does this by making hormones that tells the body what to do.
Sometimes the thyroid glands get a bit too excited and starts making too much of these hormones and when this happens, it’s like your body is in overdrive! It’s like your body engine is revving too high.
Understanding The Thyroid Gland
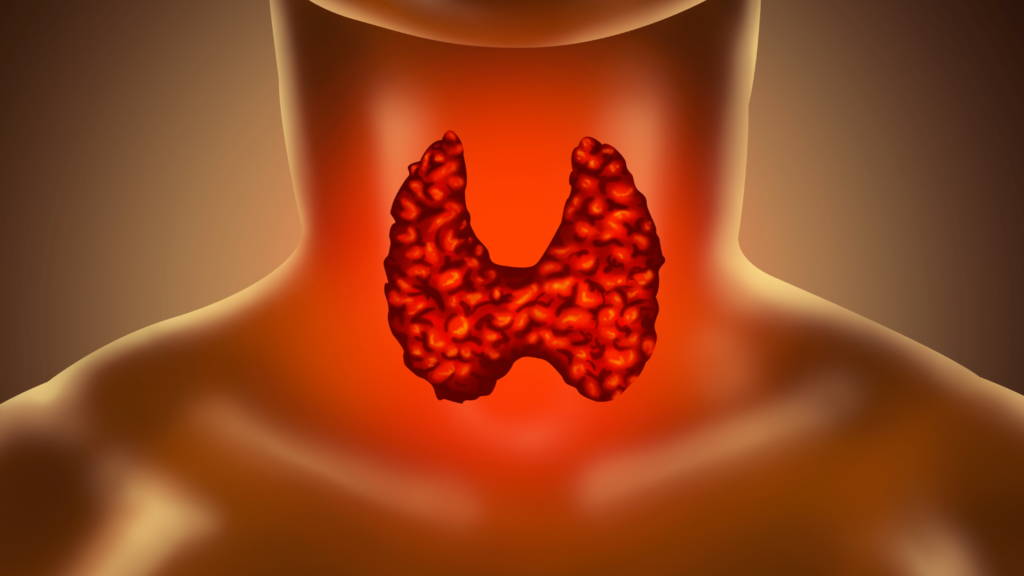
The thyroid gland is in the front of the neck right underneath the Adam’s apple. It’s a very small gland that looks like a butterfly, but it does a powerful job in the body. If you look at the image below, it shows you a clear image of what the thyroid looks like and where’s it located. The main job for the thyroid is to produce something called hormones. The hormones send me messages to other parts of the body to tell them what they should be doing.
Now let’s talk about these hormones and what they create. The thyroid glands make two important hormones that are called thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3). You can think of them as the superheroes of your body.
Why are these hormones so important?
These hormones are so important because they act as traffic signals in our body. They help regulate things like how fast your heart beats, how fast your body burn energy for food, and how your body temperature is controlled. Let’s explore some of the most important duties of the T3 and T4 hormones.
- Metabolism Heaven: Think of metabolism as the engine that keeps your body running. The thyroid hormones get the engine going, helping you convert food to energy faster. This mean the more energy you have; the more energy you will have to do the things you enjoy doing.
- Growth and Development: Think of a plant who needs sunlight to grow, your body needs thyroid hormones to grow and develop correctly. As you went from a baby to a big kid to an adult, it was these hormones that ensured you grow healthy and strong.
- Brain Power: Thyroid hormones help your brain develop and works at its best. It is kind of like the better your hormones work the better you can think clearly, recall things, and grasp new things you enter daily.
- Healthy Heart: The heart’s role is to pump blood to every part of your body and the thyroid hormones help keeps your heart beating just at the right speed making sure it stays healthy and strong.
What Causes Hyperthyroidism?
Are you struggling with hyperthyroidism and want to know what causes this disease. When your thyroid gland goes into overdrive and works super-duper fast, you want to know why and how this happens. Well, let’s find out!
Common Causes of Hyperthyroidism:
- A confused Immune System: Your immune system fights off bad germs like viruses and bacteria and sometimes our immune system gets a bit confused and instead of protecting us, it attacks our thyroid gland. When the immune system mistakenly attacks the thyroid gland, it can cause a condition called autoimmune thyroiditis or Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. And eventually this can damage the thyroid gland making is difficult for the gland to perform it job.
- Grave’s Disease: Grave’s disease takes place when the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks the thyroid gland because it thinks it trying to harm the body it specifically targets a protein called thyroid-stimulating hormone receptor (THSR) and this receptor is responsible for regulation the production of the thyroid hormones. The disease produces antibodies that mimic the action of TSH and this cause an over production of the hormone which then cause the gland to overwork.
- Nodules: Imagine your thyroid gland as a tiny factory in the neck that create thyroid hormones. Sometimes in this little factory little lumps or bumps can form which are called nodules. Don’t think of them as being bad but if too many of them grow or grow too big they can start affecting the thyroid gland by making extra thyroid hormone that the body not capable of handling successfully. But you can think of iodine, kind of like pouring too much syrup on your waffles. When this happens, it confuses the thyroid gland and provokes it to work harder and produce too many hormones.
- Too Much Iodine: Iodine helps your thyroid gland make the right amount of thyroid hormone and keep your body running smoothly. Think of food sources such as: seafood, dairy products, salt, vitamin B12, and zinc.
Signs and Symptoms
Hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid) can cause a wide range of symptoms. We will talk about a few of them in detail.
- Weight Loss – No matter how much you eat; you may find yourself losing weight quickly. It’s like a car is burning fuel quickly even though it’s not stopping at the gas station.
- Increased appetite –You may feel hungrier than usual because of the increase metabolism. It’s like the car keeps feeling hungry for fuel because it’s using it up so fast.
- Rapid Heartbeat (Palpitations) – Your heart may feel like it’s racing or beating irregularly. It’s like the engine is revving too fast making the car feel like it’s racing even when it’s parked.
- Feeling Jittery or Anxious – Excess thyroid hormone can make you feel nervous. It’s like the car’s driver feels nervous because the car is going too fast, and you are having a hard time controlling it.
- Trouble Sleeping: Hyperthyroidism disrupt your sleep patterns making it difficult to fall asleep or stay asleep. It’s like the car’s engine is making too much noise, keeping the driver awake at night.
- Change In Bowel Habit: Some people experience diarrhea or more frequent bowel movements. It’s like the car needs to make more pit stops because everything is moving too quickly inside.
- Tremors: You might notice trembling or shaking in your hands or fingers due to the increase in the metabolic activity. It’s like the car’s steering wheel is shaking because the engine is running too fast.
These symptoms can vary in severity from person to person and not everyone will experience all of them. But if you notice any of these symptoms persisting or start to interrupt your daily life consult your healthcare provider for testing and treatment.
Diagnosis and Evaluation of Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism is a condition characterized by an overactive thyroid gland, leading to an excessive production of thyroid hormones. Diagnosis and evaluation of hyperthyroidism involve a combination of medical history, physical examination, and laboratory tests.
During the physical examination, the healthcare provider may check for signs such as an enlarged thyroid gland (goiter), rapid pulse, tremors, or eye changes (in Graves’ disease). Here’s an overview of the process:
- The Thyroid Function Test: This is one of the most crucial and common tests performed. There are different types of thyroid function tests, but the main ones are:
- TSH Test (Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone): This test checks how much of a special hormone your brain sends to your thyroid. It sends a message from your brain telling your thyroid gland to do its job. This hormone is made by a gland in the pituitary gland. To perform the TSH test a small amount of blood is taken and the sample sent to the lab. Normal TSH level can vary depending on age and gender but falls between 0.4 and 4.0 Mu/L.
- T4 Test (Thyroxine): This test measures how much hormone the thyroid gland is making. The thyroxine plays an important part in regulating your body’s metabolism, heart rate, body temp, and energy levels. This test is performed by using a small amount of drawn blood and tested in a lab. Normal range of T4 is 4.5 to 12.5 mcg/dL or 58 to 161 nmol/L. Again, these factors can change depending on age, gender, and current health conditions.
- T3 Test (Triiodothyronine): This test measures the level of triiodothyronine another hormone made by the thyroid gland. T3 helps control metabolism, energy creation, and growth and development of the body and it works closely with T4. This test is performed by taking blood that is sent to the lab for testing. Normal T3 levels depends on age, gender, and health condition. But the normal range runs between 80 to 200 ng/dL or 1.2 to 3.1 nmol/L.
- Radioactive Iodine Uptake Test: This test measures the amount of radioactive iodine taken up by the thyroid gland. This test involves a doctor using a small amount of iodine called radioactive iodine. You take a capsule that is filled with radioactive iodine and wait between 4 hours to one day before the test is performed. This test will tell the doctor how much your thyroid gland has absorbed. If it absorbed too much or not enough it will tell if you have an overactive or underactive thyroid gland.
- Thyroid Ultrasound: A thyroid ultrasound is like how an ultrasound is performed on a pregnant woman. During the ultrasound a device called a transducer is placed on the skin over the gland and sound waves create images of the thyroid gland and the lymph nodes. This test helps determines the size, shape, and quality of the thyroid gland. The doctor will take not of the condition of the thyroid gland to determine if there’s some abnormities going on.
These test methods help prove any issue with your thyroid as it relates to hyperthyroidism. Fine-needle aspiration biopsy, MRI, and CT are other tests that can be considered for understanding the condition of the thyroid gland.
Thyroid Stimulation Hormones (TSH) test is considered the most common and safest test performed for testing the activity of the thyroid functions. This test is considered safe, non-invasive, and easily available. I advise you as the patient to do your research and determine the best test for you and express this with your doctor behind your decision.
Treatment Options
Hyperthyroidism can be a temporary condition and can go away on its own. When considering the treatment options for yourself, you must take into consideration your age, other medication you’re taking at the time, and other health condition. We will explore the three most common treatment options offered to patients.
- The first option is Anit-Thyroid Medications: These medications are used to treat condition where the thyroid gland produces too much thyroid hormone. It works by decreasing the among of hormones produced in the body. Some of the well know antithyroid medications are:
- Methimazole: This medication helps to cut down the level of thyroid hormones in the bloodstream. This medication works by telling the thyroid gland to slow down producing thyroid hormone. Methimazole in high doses can increase the risk of the disease developing in the baby which is why propylthiouracil is prescribed. If methimazole is ever prescribed and needed during pregnancy, it will be given in the second trimester. And it is because the important developmental period has passed, risk of birth defects decreases, and it is most effective during this period.
- Propylthiouracil: This medication is comparable to methimazole but is prescribed to pregnant when methimazole is not suitable. This medication helps bring the thyroid hormones back to normal levels. This medication is preferred over any other medication during pregnancy. Because the low risk of birth defects happening. PTU is usually taken on a short-term basis until other options become available but can be taken for long-term.
- Carbimazole: This drug can be a bit tricky and risky because the body changes it into methimazole after consuming it. This medication comes in two forms a pills and tablets. This drug is not recommended for use during pregnancy especially in the first trimester when the fetal is developing.
- Beta-Blocker: Beta-blocker helps us controls the adrenaline hormone. This is the hormone that get us prepared for acting at any time and very quickly. Beta-blockers blocks this action. Beta-blockers help slow down your heart rate and lower your blood pressure. This medication is prescribed to patients with hyperthyroidism to help relieve symptoms such as: rapid heart rate, tremors, and anxiety by blocking the effects of the excess thyroid hormones on the body. Propranolol, atenolol, and metoprolol is normally used to manage hyperthyroidism. Propranolol is mostly preferred due to its blockage of beta-1 receptor (beta-1 receptors primarily leads to an increase in heart rate) and beta-2 receptor (beta-2 receptors causes relaxation of smooth muscles, release of glucose for energy production during times of need).
- Radioactive Iodine Therapy: Radioactive treatment involves taking radioactive form of iodine that absorb by the thyroid gland. This treatment works by the patient’s swallowing iodine that will target the cells in the thyroid gland and shrink the thyroid gland or kill the unhealthy cells. This type of treatment job is to slow down the overactive gland.
- Thyroidectomy: A thyroidectomy is a surgery when the doctor take out all or part of the thyroid gland. This treatment will be recommended when other treatments are not suitable or effective, large goiters, or suspicion of thyroid cancer. The drawback of this treatment is that you will have to be on hormone replacement for the rest of your life.
Depending on the condition of your thyroid gland and other conditions will determine the best treatment for you to undertake. But always consider the best options for you and not just allow someone to make the discission for you.
Conclusion:
Understanding the thyroid gland and its role in the body is important. This small member of the body plays a vital part in producing hormones that helps every other organ in the body. Treatment is only half of the correction. You should consider lifestyle changes and learn how to keep your body out of the read when it comes to hyperthyroidism. If you suspect you or someone you may know, be experiencing signs of hyperthyroidism, seek medical help sooner than later. Don’t let lab created medication be your first option when considering treatment. So often conditions can be reversed with nature herbs, lifestyle change, and eating habits.
Make sure you weigh out all your options when it comes to you taking any medication. You can never assume the doctor knows your body better than you. It is up to you to take control of your health and not 100% put all your trust in your doctor. This is your life, your health and it’s your responsibility to see that you are getting the best care possible. Don’t let your health be a mystery start your journey of awareness today!